
API Contracts in Microservices Communication
🔗 Role in Microservices — API contracts define the expected interactions between microservices, ensuring that each service communicates correctly with others. This is crucial in a microservices architecture where services are independently developed and deployed.
Read More
Hinted Handoff in System Design
🔄 Definition — Hinted handoff is a technique used in distributed systems to improve write availability and ensure data durability when some nodes are temporarily unavailable.
Read More
Consistent Hashing in System Design
🔄 Definition — Consistent hashing is a distributed hashing technique used to distribute data across multiple nodes in a network, minimizing the need for data redistribution when nodes are added or removed.
Read More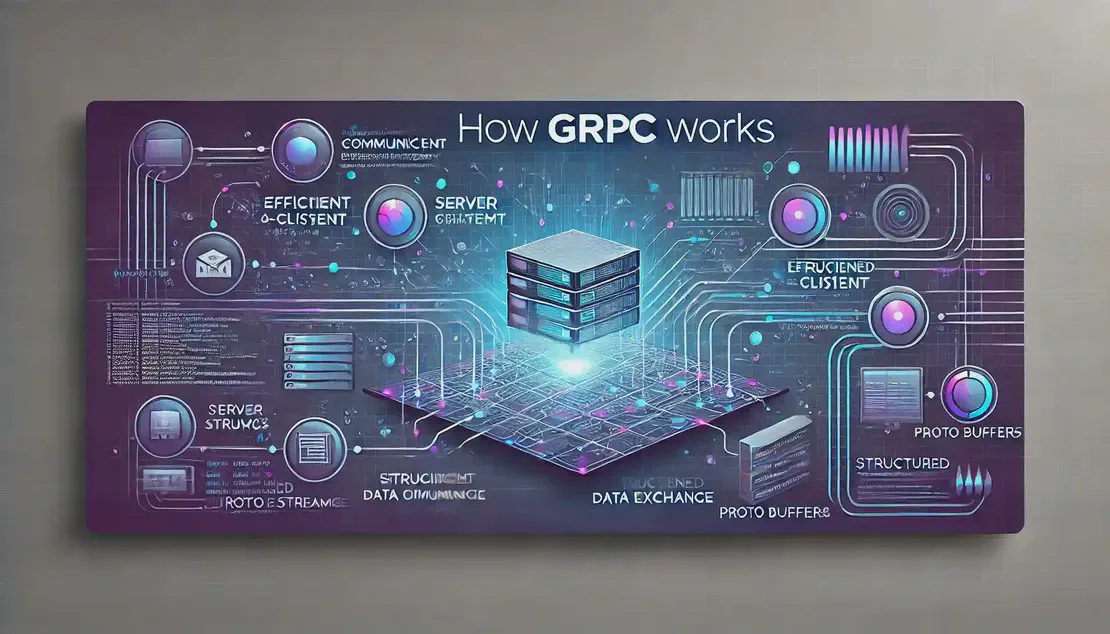
How gRPC Works
🔧 Architecture — gRPC is a high-performance, open-source RPC framework that uses HTTP/2 for transport and Protocol Buffers for message serialization. It allows client applications to call methods on a server application as if they were local objects.
Read More
Understanding CI/CD in Software Development
🔄 CI/CD Definition — CI/CD stands for Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery/Deployment. It is a set of practices that automate the integration of code changes and the delivery of software updates.
Read More
Docker Architecture Explained
🖥️ Client-Server Model — Docker uses a client-server architecture where the Docker client communicates with the Docker daemon to manage containers.
Read More
Kubernetes Architecture Explained
🔧 Control Plane — The control plane manages the overall state of the Kubernetes cluster. It includes components like kube-apiserver, etcd, kube-scheduler, and kube-controller-manager, which handle tasks such as API management, data storage, scheduling, and running controller processes.
Read More
Timeout Pattern in Microservices
⏳ Timeout Pattern — The timeout pattern in microservices is a design strategy used to handle delays and failures in service communication by setting a maximum wait time for responses.
Read More
Service Discovery in Microservices
🔍 Definition — Service discovery is a mechanism that allows microservices to locate and communicate with each other within a distributed system. It is essential for managing the dynamic nature of microservices environments.
Read More
Chaos Engineering in Microservices
🔍 Definition — Chaos Engineering is a discipline that involves experimenting on a software system in production to build confidence in the system’s capability to withstand turbulent conditions.
Read More
Main API Architecture Styles
🔄 REST — REST (Representational State Transfer) is a stateless architectural style that uses standard HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE. It is simple, scalable, and flexible, supporting various data formats such as JSON and XML. However, it lacks a clear contract and has limited support for complex queries.
Read More
Best Practices for Managing Secrets in Microservices
🔐 Centralized Management — Use centralized secret management systems like HashiCorp Vault or AWS Secrets Manager to securely store and manage secrets. This helps in maintaining a single source of truth and simplifies access control.
Read More
Distributed Tracing in Microservices Explained
🔍 Definition — Distributed tracing is a method used to track and observe application requests as they move through distributed systems or microservice environments.
Read More
Service Mesh: Managing Microservices Communication
🔍 Definition — A service mesh is an infrastructure layer that manages communication between microservices in a distributed system, providing tools for traffic management, security, and observability.
Read More
Sidecar Pattern in Microservices
🔄 Definition — Event sourcing is a pattern where the state of a business entity is stored as a sequence of events, rather than just the current state.
Read More
Event Sourcing in Microservices
🔄 Definition — Event sourcing is a pattern where the state of a business entity is stored as a sequence of events, rather than just the current state.
Read More
Understanding Two-Phase Commit in Microservices
🔄 Protocol Overview — The Two-Phase Commit (2PC) protocol is a distributed algorithm used to ensure that a transaction is either committed or aborted across all participating nodes in a distributed system.
Read More
Understanding the CQRS Pattern
🔄 Definition — CQRS stands for Command Query Responsibility Segregation, a pattern that separates the responsibilities of handling commands (write operations) and queries (read operations) in a software system.
Read More
Understanding the Saga Pattern in Microservices
🔄 Definition — The Saga pattern is a design pattern used to manage distributed transactions in microservices by breaking them into a series of smaller, local transactions.
Read More
Managing Transactions in Microservices
🔄 Distributed Transactions — Managing transactions in microservices often involves distributed transactions, which can be complex due to the need to maintain consistency across multiple services.
Read More
Understanding the Circuit Breaker Pattern
🔌 Definition — The Circuit Breaker Pattern is a design pattern used in software development to prevent an application from repeatedly trying to execute an operation that is likely to fail.
Read More
Understanding Event-Driven Architecture
🔄 Definition — Event-driven architecture (EDA) is a software design model that focuses on the publication, capture, processing, and storage of events, allowing systems to respond in real-time or near-real-time.
Read More